QatarEnergy has signed an agreement with CSSC Hudong zhonghua shipbuilding for eight 271,000 m3 Q-Max ultra-large liquefied natural gas (LNG) carriers, which are expected to be delivered between 2028 and 2029.
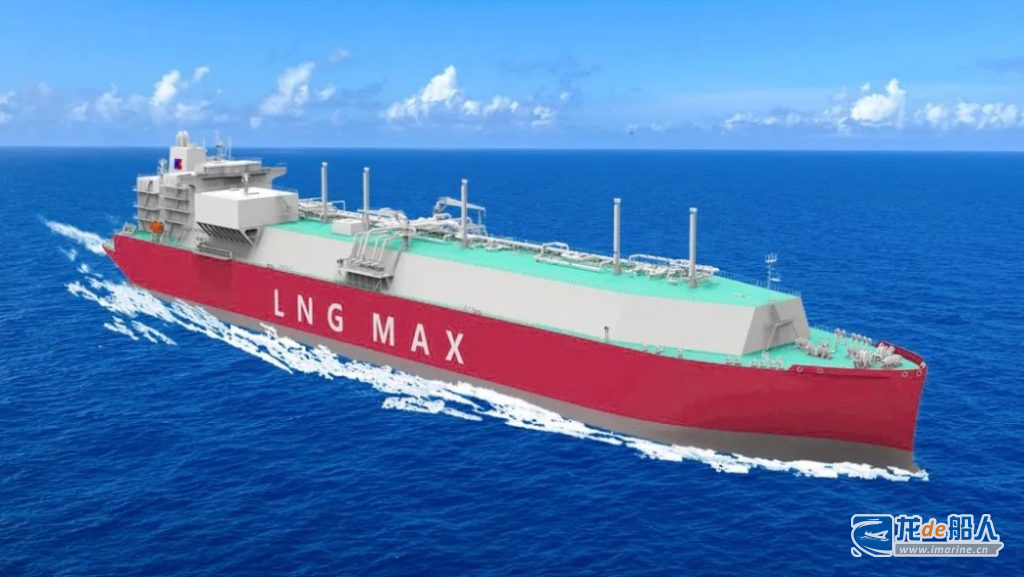

The Q-Max vessels are part of QatarEnergy’s shipbuilding program–Hundred Ships Program and will primarily serve Qatar Energy’s long term transactions related to the North Field Expansion Project, including transactions with Chinese customers. Currently, QatarEnergy will enter into fixed-term charter contracts with shipowners for the eight new vessels, in the same way as it did for the vessels it ordered in the first phase of the Hundred Ships Program.
The order was reportedly finalized last month (late 2023) at an undisclosed deal price. The cost of a conventional 174,000 m3 LNG carrier of Chinese shipyard is more than $235 million, while it is $265 million of a South Korean shipyard. The cost of the Q-Max LNG carriers mentioned above could exceed $300 million per ship, which would make Hudong zhonghua’s order for eight new vessels worth more than $2.4 billion (RMB 17.183 billion).
In September 2023, it was announced that QatarEnergy was ordering 15 Q-Max ultra-large LNG carriers from Chinese and South Korean shipyards, with the final contract expected to be finalized by the end of 2023, and the value of the order could reach billions of dollars. According to the latest news, eight of the vessels have now been confirmed to be undertaken by Hudong Zhonghua, while the other seven are likely to be undertaken by South Korean shipyards.
QatarEnergy has signed an agreement with Hudong Zhonghua for the ” Hundred Ships” Program as early as 2020, as its annual production capacity and secures shipping capacity increased, including for the North Field Expansion Project.
So far, including the latest order, Hudong Zhonghua will build a total of 20 LNG carriers for QatarEnergy. It is worth noting that the 271,000 m3 vessels signed are the world’s largest LNG carriers to date, with dual-fuel low-speed engine propulsion and NO96 Super+ envelope system, and have been granted Approval-in-Principle (AiP) in September 2023 by ABS, LR, BV, and DNV.
With an overall length of 344 meters, a beam of 53.6 meters and a design draft of 12.0 meters, the vessel is slightly smaller than Qatar’s Q-Max and can normally dock at Qatar’s LNG terminals. Hudong-Zhonghua indicated that the vessel offers excellent ship-to-shore compatibility by being able to dock at more than 70 LNG terminals on major trade routes.
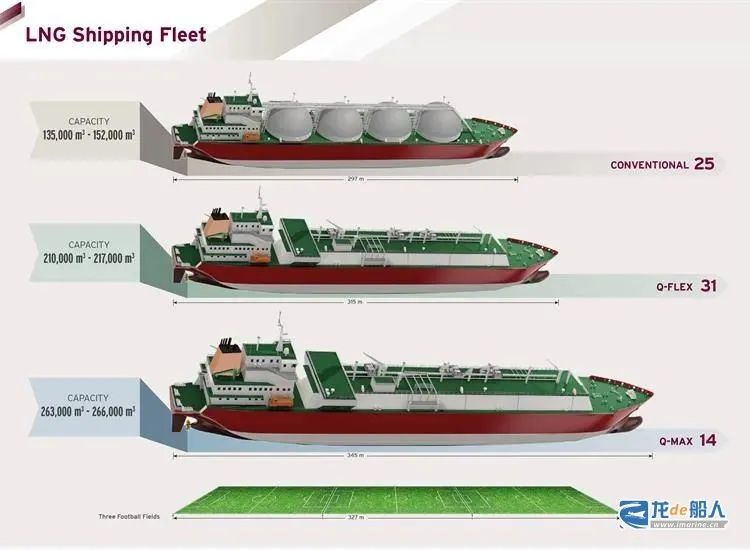
QatarEnergy is known to have ordered two types of ultra-large LNG carriers from South Korean shipyards, namely 31 Q-Flex vessels and 14 Q-Max vessels, which were built by Hanwha Ocean (formerly Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine) and Samsung Heavy Industries between 2008 and 2010, respectively.
The Q-Flex has a cargo tank capacity of 210,000 m3 and the Q-Max has a cargo tank capacity of 266,000 m3. The Q-Max is the world’s largest completed LNG carrier, with a length of 345 meters, a breadth of 53.8 meters and a draft of 12 meters. The “Q” stands for Qatar and the “Max” stands for the largest size vessel that can dock at the Qatar LNG terminal.
In addition to Hudong Zhonghua, QatarEnergy plans to place orders with South Korea’s Samsung Heavy Industries, Hanwha Ocean and HD Hyundai Heavy Industries for the second phase of the “Hundred Ships Program”.
In October 2023, QatarEnergy officially signed a contract with HD Hyundai Heavy Industries for the construction of 17 174,000 m3 LNG carriers, with an order value of about $3.9 billion, at a cost of only $229 million per ship. In addition, QatarEnergy is expected to award more contracts this year under the “Hundred Ships Program”. In addition to HD Hyundai, Hanwha Ocean and Samsung Heavy Industries are also negotiating with QatarEnergy and are expected to sign final contracts this year.


